Adventures In Power Plant Engineering
Shift Duties, Camaraderie And Other Shenanigans …..
Portugal
Current Country
Spain
Next Country
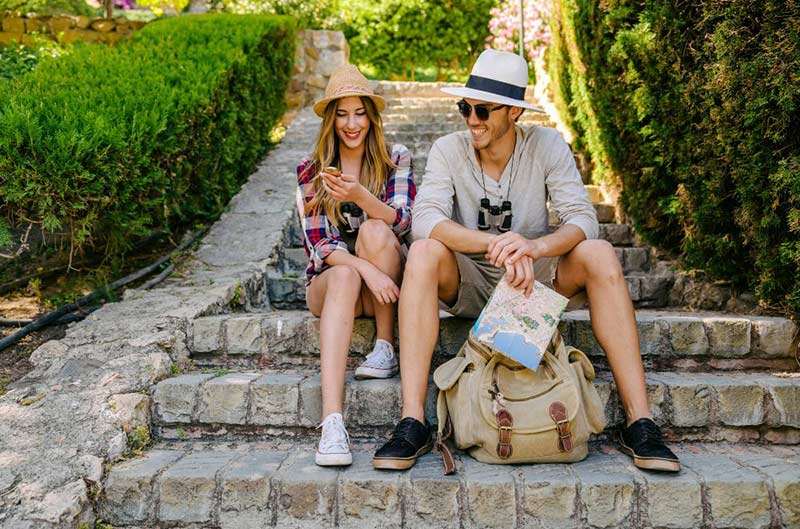
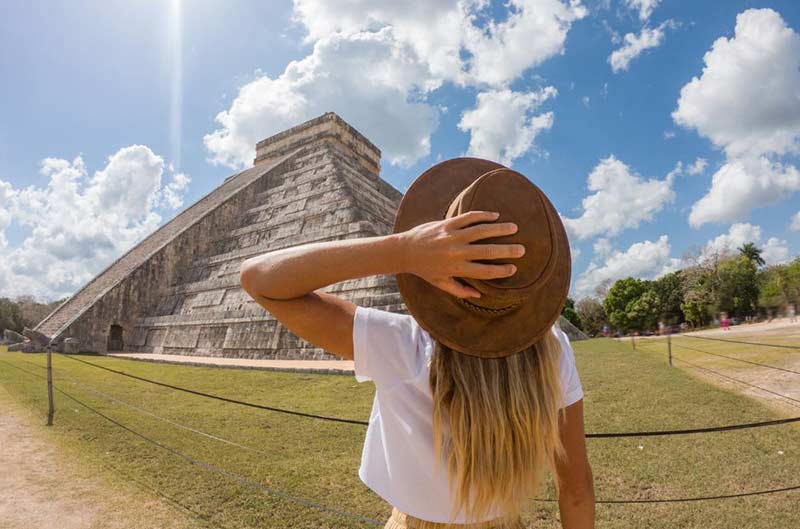



Welcome To Our World
Hi! So, that’s my girlfriend and me, and we travel the world for fun whilst we live off our rich parent’s hedge fund. I know, pretty cool, right?
We have been travelling around the world now for a little over 7 years, and we have accumulated a wealth of travel experience, tips, tricks and advice.
And we’re here to share everything we know with you.
Welcome to Travel Crush x
Fresh From Our Blog.......

Does Anybody Work Here Anymore?
Well, it’s true. The stationary engineer / boiler operator is a dying trade. There is not enough young people interested in this type of work.

How To Choose The Best Backpack For Travel
These days, there are so many backpacks out there that it can be confusing knowing how to pick the right one.
There’s actually a science to knowing what the best travel

Essential Travel Apps Everyone Needs On Their Phone
There’s no shortage of travel apps cluttering up the Android and Apple marketplaces these days — and that’s a problem, as most of them are terrible. Sorting out useless ones from
Looking for some extra travel tips and tricks?
Why not check out our travel resources page and our ultimate travel tips
Inspiration for your next adventure
Asia Travel
Europe Travel
We've been featured In